1.Generation and conduction of cutting heat
The metal is cut, under the action of a tool, elastic and plastic deformations occur while power consumed, which cut An essential source of heat reduction.
Also, the chips mixed The friction between the front tool face, workpiece, and the back tool face. It consumes power and generates a lot of heat.
Therefore, there are three heating areas in cutting, namely, shear surface, the contact area between the chip and front tool face, back tool face, and transition surface contact area.
The contact area between the chip and front tool face, back tool face, and transition Surface contact area.
As shown, there are three heating zones and three deformations. Region correspondence. So, the source of the cutting head. The work of chip deformation and the work of friction between the front and back surfaces.
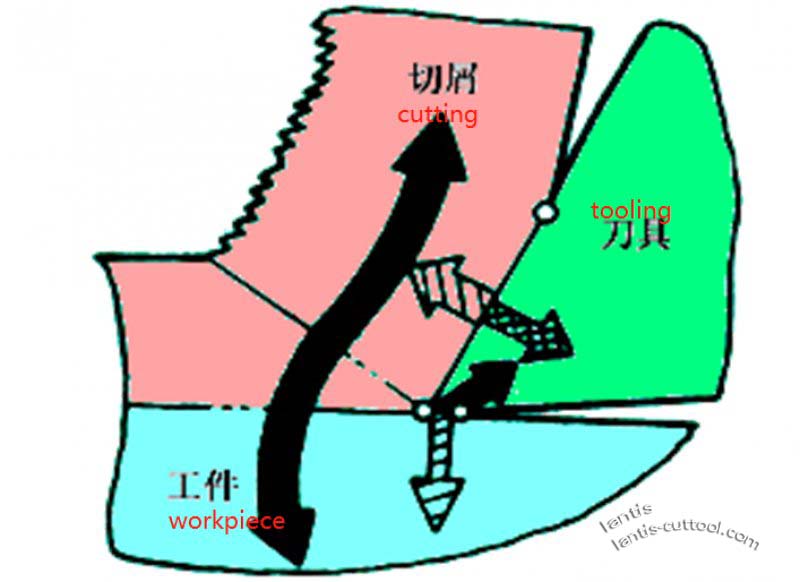
2.Measurement of cutting temperature
Although the cutting heat is the root cause of the rise of decreasing temperature, it is the cutting temperature that directly affects the cutting process.
The cutting temperature generally refers to the average temperature of the contact area between the rake face and the chip. The average temperature of the rake face can be approximated.
It considered as the sum of the average temperature of the shear surface and the friction temperature between the rake face and the chip contact surface.
3.The main factors that affect the cutting temperature
According to the theoretical analysis and a lot of experimental research, the cutting temperature is mainly affected by cutting parameters and tool geometry
Parameters, workpiece materials, tool wear, and the effects of cutting fluid, following the analysis of these significant factors.
(1) the influence of cutting parameters on cutting temperature
The impact of each element on the cutting temperature should be analyzed mainly from the heat produced in the unit time by these factors. And the amount of heat coming out of it.
\If the amount of heat produced is higher than the amount of heat transferred; these factors will cause the cutting temperature to increase; certain factors cause the output heat to grow, then these factors will cause the cutting temperature to reduce
The cutting speed has the most significant influence on the cutting temperature.
With the increase in cutting speed, the cutting temperature rises rapidly.
The effect of feed rate is secondary, while the area of heat dissipation and the amount of heat produced are also changed when the force ap is changed
Therefore, ap has little effect on cutting temperature.
(2) the influence of tool geometry parameters on cutting temperature
The cutting temperatureθ decreases with the increase of Rake Angle γo. This is because when the rake angle increases, the unit cutting force under The cutting heat produced by cutting reduced.
But the influence of the rake angle greater than 18°~20°on the cutting temperature. Noise reduction, this is because the wedge angle is smaller and so that the heat loss volume reasons.
When the Principal Deflection Angle R increases, the working length of cutting edge shortens, the angle of tooltip decreases, and the cutting width aw decreases
Lowering thickness AC increases so that the cutting temperature will rise.
The negative Chamfer bγ1 changes in the range of (0-2) f, and the radius of ARC re changes in the field of 0-1.5 mm.
Basically does not affect the cutting temperature. Because of the negative chamfer width and tip radius increase, will make plastic change. On the other hand, both of them can improve the heat dissipation condition of the cutting tool
There is also an increase in the heat; the two tend to balance, so the impact on the cutting temperature is minimal.
(3) the influence of tool wear on cutting temperature
The higher the cutting speed is, the higher the cutting temperature is
The greater the impact. Alloy Steel Strength, the thermal conductivity of small, so when cutting alloy steel tool wear on
The effect of lowering temperature is higher than that of carbon steel.

(4) the influence of workpiece material on reducing the temperature
The higher the strength and hardness of the workpiece, the higher the power consumption, and the higher the cutting temperature. Heat conduction
Great rate, excellent heat dissipation, low cutting temperature.
(5) the effect of cutting fluid
The influence of cutting fluid on cutting temperature is related to the heat conductivity, specific heat, flow rate and pouring mode of cutting fluid
And its own temperature. From the thermal conductivity, oil cutting fluid as an emulsion, emulsion
Water-based cutting fluid is inferior to chemical liquid.
4.Distribution of cutting temperature
(1) the temperature at each point on the shear plane is almost the same.
(2) the highest temperature on the front and back surfaces is not on edge but on the corner at a certain distance This place.
(3) in the shear zone, the temperature gradient in the direction of the vertical shear surface is enormous.
(4) the temperature gradient on the bottom layer of the chip near the rake face is considerable, 0.1-0.2 from the rake face MM, the temperature could drop by half.
(5) the contact length of the flank is small, so the temperature rise and fall are accomplished in a short time.
(6) the lower the thermal conductivity of the workpiece material, the higher the temperature of the cutting tool’s front and back surfaces.
(7) the more significant the plasticity of the workpiece, the higher the contact length on the rake face, and the distribution of the cutting temperature
On the contrary, the higher the Brittleness of the workpiece material, the closer the point of the highest temperature is to the cutting edge.
5. The effect of cutting temperature on workpiece, tool and cutting process
High cutting temperature is the leading cause of tool wear, which will limit the productivity increase Will reduce the processing accuracy; the surface has been processed to produce residual stress and other defects.
(1) the influence of cutting temperature on material strength and cutting force of the workpiece
Although the cutting temperature is very high, the cutting temperature does not affect the hardness and power of the workpiece material
Very Large, the effect on the stress in the shear zone is not apparent.
(2) the impact on the cutting tool material
It is beneficial to improve the toughness of cemented carbide by increasing the cutting temperature properly. Because at high temperatures,
the strength of the hard alloy is higher, not comfortable to break, wear resistance will also be reduced.
(3) the effect on the dimensional accuracy of the workpiece
The workpiece itself expanded by heat; the diameter changed, the required precision can not be reached after cutting; the cutter Rod is heated
The diameter decreases as the actual depth of cutting increases and the workpiece become longer when heated, but is fixed to the machine tool Can Not be free to stretch on the bending, turning the inner diameter of the workpiece increased.

Leave A Comment